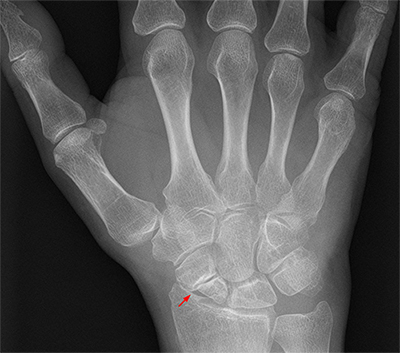
Scaphoid Fracture
A scaphoid fracture refers to a break in one of the central wrist bones, commonly caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. Breaking your fall with your hand is often an uncontrollable a reflex response, unfortunately the hand is composed of many small fragile bones which can break under excessive force. A fracture of the scaphoid typically produces pain on the thumb side of the wrist joint aggravated by wrist movement and gripping. Scaphoid fractures can be a little tricky as they don’t always cause intense pain and noticeable deformity like typical bone fractures. Due to this, many people don’t actually realise that they have broken their scaphoid. Despite this, a scaphoid fracture is a serious injury and requires immediate medical attention. If it goes ignored and untreated fragments of the bone may fail to join back together and cause lasting wrist problems. This is a serious consequence which will prolong your recovery and may require surgery or alternative treatments to stimulate healing. A physiotherapist can assist in the management of a scaphoid fracture by encouraging the natural bone healing process and strengthening the wrist muscles for lasting protection.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a nerve entrapment disorder that causes pain, sensory changes and a loss of function within the hand and wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the median nerve as it runs through a very narrow tunnel walled by wrist bones and ligaments (called the carpal tunnel). Unfortunately, this nerve has to share the tunnel with 9 large tendons that move the fingers. If any of these tendons become inflamed, the tunnel becomes too cramped and the median nerve gets compressed. Compression of any nerve can interfere with the messages or signals it transmits resulting in tingling, loss of strength or pain. If you suspect carpal tunnel syndrome you should avoid any activities which cause your pain, or numbness and tingling to worsen. From their assessment, a physiotherapist will be able to determine an appropriate treatment plan, which can involve exercises, activity modification or splinting of the wrist and hand.
