Ligament Injury/Ankle Sprain (Rolled Ankle)
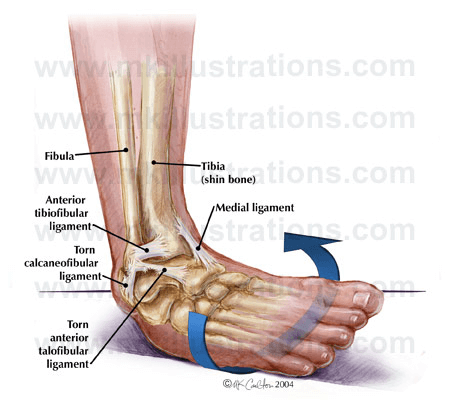 A lateral ligament injury refers to a strain or tear of one or more of the ligaments on the outside Lateral aspect of the ankle. The lateral ligaments consist of three ligament bands, providing stability to the outside of the ankle joint. These ligaments are referred to as the lateral ligament complex. Injuries to the lateral ligaments occur when they are overstretched (strained/sprained). This occurs when the foot and ankle are forcibly rolled inwards and is colloquially referred to as a “rolled ankle”. The ankle can be rolled during sudden changes in direction, on uneven surfaces, or treading on a ball or opponent’s foot. The initial sensation after a lateral ligament sprain is pain on the outside and front of the ankle. Some people also report an audible snap, crack or tear. Depending on the severity of the injury, the outside and front of the ankle may swell and you can have difficulty walking due to pain. Swelling can be immediate or occur over a period of hours. Occasionally a patient will report that the ankle feels weak. Bruising may develop which can extend up the leg and down to the toes. Most lateral ligament injuries heal within a matter of weeks depending on the extent of damage. Surrounding structures that may also be injured include bone, cartilage and muscle tendons. Injuries to these structures often produce persistent pain and swelling which may slow recovery. Incorrect diagnosis or poor management of your injury may result in reduced range of movement, weakness and an increased chance of reinjuring the ankle in the future. Physiotherapy treatment involves restoration of full range of motion, strengthening the muscles around the ankle, and improving the proprioception (balance) with specific exercises. Preventative measures may also be recommended such as taping or a brace for the ankle. Treatment also involves electrotherapy, joint mobilisations, soft tissue massage and pain management.
A lateral ligament injury refers to a strain or tear of one or more of the ligaments on the outside Lateral aspect of the ankle. The lateral ligaments consist of three ligament bands, providing stability to the outside of the ankle joint. These ligaments are referred to as the lateral ligament complex. Injuries to the lateral ligaments occur when they are overstretched (strained/sprained). This occurs when the foot and ankle are forcibly rolled inwards and is colloquially referred to as a “rolled ankle”. The ankle can be rolled during sudden changes in direction, on uneven surfaces, or treading on a ball or opponent’s foot. The initial sensation after a lateral ligament sprain is pain on the outside and front of the ankle. Some people also report an audible snap, crack or tear. Depending on the severity of the injury, the outside and front of the ankle may swell and you can have difficulty walking due to pain. Swelling can be immediate or occur over a period of hours. Occasionally a patient will report that the ankle feels weak. Bruising may develop which can extend up the leg and down to the toes. Most lateral ligament injuries heal within a matter of weeks depending on the extent of damage. Surrounding structures that may also be injured include bone, cartilage and muscle tendons. Injuries to these structures often produce persistent pain and swelling which may slow recovery. Incorrect diagnosis or poor management of your injury may result in reduced range of movement, weakness and an increased chance of reinjuring the ankle in the future. Physiotherapy treatment involves restoration of full range of motion, strengthening the muscles around the ankle, and improving the proprioception (balance) with specific exercises. Preventative measures may also be recommended such as taping or a brace for the ankle. Treatment also involves electrotherapy, joint mobilisations, soft tissue massage and pain management.
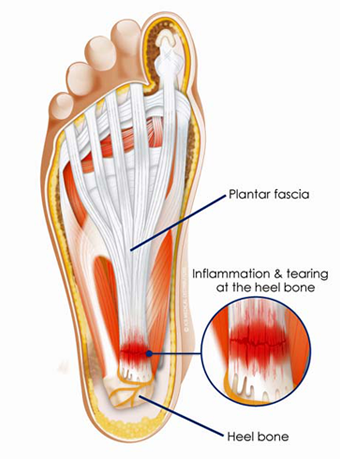
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is an overuse injury of the fibrous sheet (plantar fascia) covering the bottom surface of the foot, the condition causes pain at the site of its attachment to the heel bone. The condition can arise from excessive stretching of the plantar fascia as it is pulled away from its attachment to the heel. This is caused by activities involving repetitive ‘toe bouncing’ seen in many dancing codes and long distance running. The pain is typically aggravated by high impact exercises involving explosion through the legs, but it can also present during the first few steps in the morning before the foot gets a change to warm up. It is important that you do not ‘run through’ the pain as you can worsen the condition. The earlier this injury is treated, the more successful the outcomes. A common and successful treatment for plantar fasciitis is the correction of foot biomechanics, as faulty mechanics can predispose a person to this condition. A physiotherapist can assess your foot and its mechanics, determine the underlying problem and treat your condition so that you can put plantar fasciitis behind you.
Achillis Tendinopathy/ Achillis Tendinitis
Achilles Tendonitis is a term that commonly refers to an inflammation of the Achilles tendon or its covering. It is an overuse injury that is common especially to joggers and jumpers, due to the repetitive action and so may occur in other activities that requires the same repetitive action.
Most experts now use the term Achilles tendinopathy to include both inflammation and micro-tears.
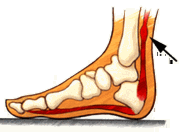
Common causes of Achilles tendinopathy are :
- Over-training or unaccustomed use – “too much too soon”
- Sudden change in training surface – e.g. grass to bitumen
- Flat (over-pronated) feet
- High foot arch with tight Achilles tendon
- Tight hamstring (back of thigh) and calf muscles
- Toe walking (or constantly wearing high heels)
- Poorly supportive footwear
- Hill running.
- Poor eccentric strength
Treatment for Achilles tendinopathy is soft tissue mobilization, correction of foot positioning, stretching of tight muscles, strengthening of weak muscles, gait re-education, advise on proper foot wear and gradual return to sport.
